Diving deep into the world of Understanding asset classes, this introduction sets the stage for an eye-opening exploration of the various types of investments and their impact on portfolios. Get ready to uncover the mysteries behind asset classes in a way that’s as cool as your favorite high school jam.
As we delve further, we’ll uncover the nuances of different asset classes and how they play a crucial role in shaping investment strategies.
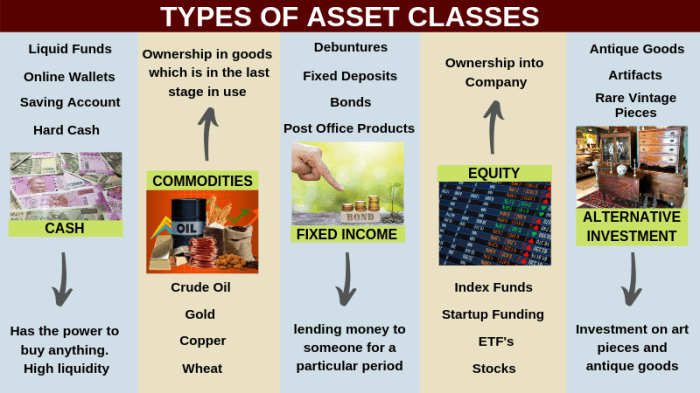
What are Asset Classes?
Asset classes are categories of investments with similar characteristics and behaviors. They play a crucial role in diversifying investment portfolios and managing risk.
Common types of asset classes found in financial markets include:
1. Stocks
- Stocks represent ownership in a company and offer potential for capital appreciation and dividend income.
- Example: Apple Inc. (AAPL), Microsoft Corporation (MSFT)
2. Bonds
- Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations with fixed interest payments.
- Example: U.S. Treasury Bonds, Corporate Bonds
3. Real Estate
- Real estate includes properties such as residential homes, commercial buildings, and land, offering rental income and potential for property value appreciation.
- Example: Apartment complexes, Shopping malls
4. Commodities
- Commodities are physical goods like gold, oil, and agricultural products, traded on exchanges.
- Example: Gold, Crude Oil, Wheat
Characteristics of Different Asset Classes
When it comes to investing, understanding the unique characteristics of different asset classes is crucial. Each asset class has its own risk-return profile, which can impact the overall performance of a portfolio. Diversification across asset classes is a key strategy to manage risk and optimize returns.
Stocks
- Ownership in a company
- Potential for high returns
- High volatility and risk
Bonds
- Debt instrument issued by governments or corporations
- Fixed interest payments
- Lower risk compared to stocks
Real Estate
- Investment in physical property
- Potential for appreciation and rental income
- Less liquid compared to stocks and bonds
Commodities
- Physical goods like gold, oil, or agricultural products
- Can act as a hedge against inflation
- Highly volatile and speculative
Alternative Investments
- Private equity, hedge funds, or cryptocurrencies
- Opportunity for diversification and potentially high returns
- Can be illiquid and carry high fees
Investment Strategies for Asset Classes
When it comes to investing in asset classes, it’s crucial to have a well-thought-out investment strategy that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Let’s explore different investment strategies tailored to specific asset classes and how investors can allocate their assets effectively.
Equities
- Equities, or stocks, are known for their potential for high returns but also come with high volatility. Investors looking for long-term growth often allocate a significant portion of their portfolio to equities.
- One common strategy is to diversify across different industries and company sizes to reduce risk. This can be achieved through investing in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track broad market indices.
- Active stock picking is another strategy where investors research and select individual stocks based on their analysis of company fundamentals and market conditions.
Bonds
- Bonds are considered a more conservative investment compared to equities, offering fixed interest payments and return of principal at maturity. Investors with lower risk tolerance often include bonds in their portfolio for stability.
- Investors can choose between government bonds, corporate bonds, municipal bonds, and high-yield bonds, each with varying levels of risk and return potential.
- Bond laddering is a strategy where investors spread out their bond investments across different maturities to manage interest rate risk and maintain a steady income stream.
Real Estate
- Real estate investments can provide passive income through rental properties or capital appreciation through property value appreciation. Investors interested in real estate can allocate a portion of their portfolio to real estate investment trusts (REITs) or real estate crowdfunding platforms.
- Diversification is key in real estate investing, with investors spreading their investments across different types of properties and geographical locations to mitigate risk.
- Some investors opt for real estate syndication, pooling funds with other investors to access larger properties or projects that would be otherwise out of reach.
Performance and Historical Trends
In the world of investing, understanding the historical performance of different asset classes is crucial for making informed decisions. By analyzing past trends, investors can gain valuable insights into how various assets have performed over time and what factors have influenced their returns.
Equities
- Equities, or stocks, have historically provided the highest returns among all asset classes over the long term.
- Market conditions, such as economic growth, interest rates, and corporate earnings, play a significant role in determining the performance of equities.
- Investors can use historical trends in stock prices to identify patterns and make informed decisions about when to buy or sell shares.
Bonds
- Bonds are known for their stability and income-generating potential, making them a popular choice for conservative investors.
- Interest rates and inflation rates are key economic factors that impact the performance of bonds.
- By studying the historical trends in bond yields and prices, investors can gauge the risk and return potential of different types of bonds.
Real Estate
- Real estate investments have shown steady appreciation over time, providing both rental income and capital appreciation.
- Economic factors such as population growth, employment levels, and interest rates influence the performance of real estate assets.
- Investors can analyze historical trends in property prices and rental yields to evaluate the profitability of real estate investments.
Commodities
- Commodities, such as gold, oil, and agricultural products, are influenced by supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and global economic conditions.
- Historical trends in commodity prices can help investors anticipate future price movements and diversify their portfolios to hedge against inflation and market volatility.
- By monitoring historical performance data for different commodities, investors can identify trends and correlations to make strategic investment decisions.