Diving deep into the world of stock portfolio analysis, this guide will take you on a journey through the ins and outs of this essential practice for investors. Get ready to explore the importance, types, tools, techniques, and strategies that make stock portfolio analysis a game-changer in the world of investing.
Importance of Stock Portfolio Analysis
Investors rely on stock portfolio analysis to assess the performance of their investments and make informed decisions to maximize returns and minimize risks. By analyzing the composition, diversification, and allocation of assets within their portfolio, investors can gain valuable insights into the health and profitability of their investments.
Benefits of Stock Portfolio Analysis
- Identifying Underperforming Assets: Through regular analysis, investors can pinpoint assets that are not performing as expected and make strategic decisions to either sell, hold, or reallocate them.
- Portfolio Diversification: Analysis helps investors determine if their portfolio is well diversified across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions to reduce risk exposure.
- Risk Management: By assessing the risk levels of individual assets and the overall portfolio, investors can adjust their holdings to achieve a balance between risk and return that aligns with their investment goals.
- Tracking Progress: Monitoring the performance of investments over time allows investors to track progress towards their financial objectives, identify trends, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Informed Decision Making: Stock portfolio analysis provides investors with the data and insights needed to make informed decisions about buying, selling, or holding assets based on their current and projected performance.
Types of Stock Portfolio Analysis
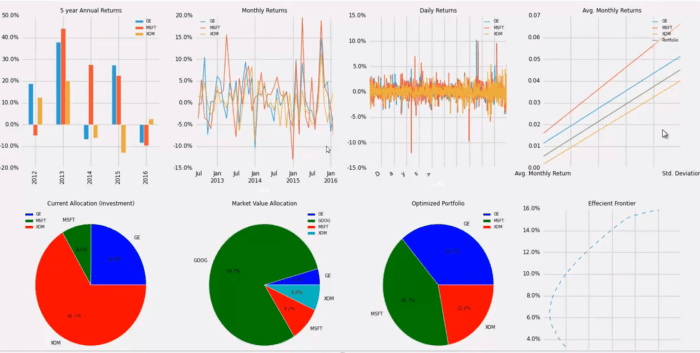
Quantitative analysis in stock portfolios involves using mathematical and statistical models to evaluate investment opportunities. This type of analysis focuses on objective data such as financial ratios, historical prices, and trading volumes to make informed decisions about buying or selling stocks.
Significance of Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis plays a crucial role in evaluating stock portfolios as it takes into consideration non-numeric factors that can impact a company’s performance. This includes aspects like management team quality, brand reputation, industry trends, and competitive positioning. By combining qualitative and quantitative analysis, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the potential risks and rewards associated with a particular stock.
Fundamental Analysis vs. Technical Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company’s financial statements, management team, industry position, and economic outlook to determine its intrinsic value. On the other hand, technical analysis focuses on studying historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends that can help predict future stock price movements. While fundamental analysis is more long-term oriented, technical analysis is often used for short-term trading strategies. Both approaches have their strengths and weaknesses, and some investors may use a combination of both to make well-informed investment decisions.
Tools and Techniques for Stock Portfolio Analysis
Stock portfolio analysis relies on various tools and techniques to help investors make informed decisions and manage risk effectively.
Diversification:
Diversification is a key strategy in stock portfolio management that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and regions. By diversifying your portfolio, you can reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio.
Common Tools for Stock Portfolio Analysis:
- Financial Ratios: Ratios like Price-to-Earnings (P/E), Price-to-Book (P/B), and Return on Equity (ROE) help investors assess the financial health and valuation of a company.
- Technical Analysis: Charts and patterns are used to identify trends and make predictions based on historical price movements.
- Fundamental Analysis: Examining a company’s financial statements, management team, and competitive position to determine its intrinsic value.
Use of Risk Assessment Techniques:
Risk assessment techniques like beta, standard deviation, and Sharpe ratio are commonly used in analyzing stock portfolios.
- Beta: Measures a stock’s volatility compared to the overall market. A beta of 1 indicates the stock moves in line with the market, while a beta greater than 1 is more volatile.
- Standard Deviation: Shows how much a stock’s price varies from its average price. Higher standard deviation implies higher risk.
- Sharpe Ratio: Helps investors evaluate the risk-adjusted return of a portfolio. A higher Sharpe ratio indicates better performance relative to the risk taken.
Strategies for Effective Stock Portfolio Analysis
Setting investment goals is crucial before diving into stock portfolio analysis. It helps investors stay focused and create a roadmap for their financial journey. Without clear goals, it’s easy to get swayed by market fluctuations and make impulsive decisions that may not align with long-term objectives.
Analyzing Historical Performance Data
When evaluating a stock portfolio, analyzing historical performance data is essential. This involves looking at past returns, volatility, and correlations with other assets. By examining how a stock has performed in various market conditions, investors can gain insights into its potential future performance.
- Look at long-term trends: Analyze how the stock has performed over different time frames, including bull and bear markets.
- Consider risk-adjusted returns: Evaluate the risk-return tradeoff by looking at metrics like Sharpe ratio and standard deviation.
- Compare with benchmark indices: Measure the stock’s performance against relevant market benchmarks to assess its relative strength.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Stock Portfolio
After conducting analysis, it’s crucial to regularly monitor and adjust the stock portfolio to stay aligned with investment goals and market conditions. Here are some tips for effective portfolio management:
- Rebalance periodically: Adjust portfolio allocations to maintain the desired risk-return profile and capitalize on market opportunities.
- Stay informed: Keep up with market news and company updates to make informed decisions about portfolio adjustments.
- Use stop-loss orders: Implement stop-loss orders to protect against significant losses and limit downside risk.
- Diversify effectively: Spread investments across different asset classes and industries to reduce concentration risk.