With Behavioral biases in investing at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Ever wondered why some investment decisions seem irrational? Let’s dive into the fascinating realm of behavioral biases in investing and uncover how our minds can play tricks on us when it comes to financial choices.
Introduction to Behavioral Biases in Investing
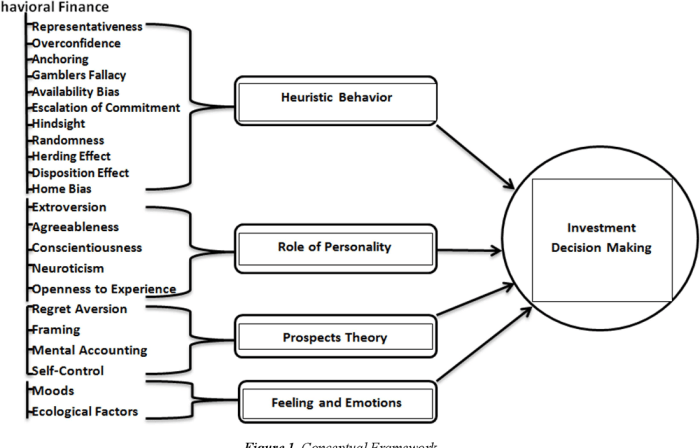
Behavioral biases refer to the systematic patterns of deviation from rationality in decision-making. In the context of investing, these biases can significantly impact how investors make choices and manage their portfolios. Understanding these biases is crucial for investors to make more informed and strategic investment decisions.
Impact of Behavioral Biases on Investment Decisions
Behavioral biases can lead investors to make irrational decisions based on emotions rather than facts. This can result in buying or selling assets at the wrong time, holding onto losing investments for too long, or being overly influenced by short-term market fluctuations. These biases can ultimately hinder portfolio performance and lead to missed opportunities for growth.
- Overconfidence Bias: Investors may overestimate their knowledge and abilities, leading them to take on excessive risks or trade more frequently than necessary.
- Loss Aversion Bias: Investors tend to feel the pain of losses more intensely than the pleasure of gains, causing them to hold onto losing investments in the hope of breaking even.
- Confirmation Bias: Investors seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs while ignoring evidence that contradicts them, leading to biased decision-making.
Types of Behavioral Biases
Behavioral biases play a significant role in shaping investment decisions. Let’s explore some of the common types of biases that investors may encounter.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias refers to the tendency of individuals to seek out information that confirms their pre-existing beliefs or opinions while ignoring contradictory evidence. In investing, this bias can lead investors to only consider information that supports their initial investment thesis, even if it may not be accurate. As a result, investors may overlook warning signs or potential risks, ultimately impacting their investment choices.
Loss Aversion
Loss aversion is the tendency for individuals to prefer avoiding losses over acquiring equivalent gains. In investing, this bias can lead investors to hold on to losing investments for too long in the hope of recovering their losses, even when it may be more prudent to cut their losses and move on. This fear of realizing a loss can prevent investors from making rational decisions and taking appropriate action to protect their investments.
Herd Mentality
Herd mentality refers to the tendency of individuals to follow the actions of the crowd without critically evaluating the information or rationale behind those actions. In investing, this bias can lead to market bubbles or crashes, as investors may blindly follow the herd without considering the underlying fundamentals of the investment. This can result in inflated asset prices or sudden sell-offs, impacting investment outcomes for individuals who simply follow the crowd.
Overconfidence Bias
Overconfidence bias occurs when individuals believe their abilities or knowledge are greater than they actually are. In investing, this bias can lead investors to take on excessive risks or make speculative trades based on their overconfidence in their own judgment. This can result in poor investment decisions and potential losses if their assumptions are proven wrong.
Recognizing Behavioral Biases in Yourself
When it comes to investing, recognizing your own behavioral biases is crucial. These biases can cloud your judgment and lead to poor decision-making, impacting your investment outcomes. By being aware of these biases, you can take steps to mitigate their effects and make more rational choices.
Methods for Identifying Behavioral Biases
- Keep a trading journal: Record your thoughts and emotions before making investment decisions. Look back at your entries to identify patterns of biased thinking.
- Seek feedback from others: Share your investment strategies with a trusted friend or advisor. They can provide an outside perspective and point out any biases they observe.
- Take a step back: When feeling strong emotions like fear or greed, pause and reassess your decisions. Emotional reactions can often indicate the presence of biases.
Tips to Overcome Biases
- Diversify your portfolio: By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce the impact of any single biased decision.
- Set clear investment goals: Define your objectives and risk tolerance in advance to prevent impulsive actions driven by biases.
- Utilize stop-loss orders: Implementing automatic sell orders can help limit losses caused by emotional trading decisions.
Importance of Self-Awareness
Understanding your own behavioral biases is the first step in becoming a more disciplined and successful investor. Self-awareness allows you to recognize when biases are influencing your choices and empowers you to take corrective action. By staying vigilant and continuously assessing your decision-making processes, you can improve your overall investment performance.
Impact of Behavioral Biases on Investment Performance
Behavioral biases can have a significant impact on investment performance, often leading to suboptimal outcomes for investors. These biases can cloud judgment, influence decision-making, and cause individuals to deviate from rational investment strategies. As a result, investors may miss out on profitable opportunities, take unnecessary risks, or make impulsive decisions that harm their overall portfolio performance.
Loss Aversion Bias:
Loss aversion bias is a common behavioral bias that can negatively affect investment performance. This bias refers to the tendency for individuals to strongly prefer avoiding losses over acquiring gains. As a result, investors may hold onto losing investments for too long in the hope of recovering their losses, even when it may be more beneficial to cut their losses and reallocate funds to more promising opportunities.
Overconfidence Bias:
Overconfidence bias can also impact investment performance by leading investors to overestimate their knowledge and abilities. This can result in excessive trading, taking on too much risk, or ignoring valuable input from financial advisors or experts. Overconfident investors may fail to diversify their portfolios adequately, leading to increased vulnerability to market fluctuations and potential losses.
Confirmation Bias:
Confirmation bias can further exacerbate the impact of behavioral biases on investment performance. This bias involves seeking out information that confirms preexisting beliefs or opinions while disregarding contradictory evidence. Investors affected by confirmation bias may overlook warning signs or negative data that could have informed more prudent investment decisions, ultimately leading to poor performance.
Strategies for Managing Behavioral Biases:
To mitigate the negative impact of behavioral biases on investment performance, investors can adopt several strategies. These include maintaining a diversified portfolio to reduce risk exposure, setting clear investment goals and sticking to a disciplined investment plan, seeking feedback from unbiased sources, and regularly reviewing and adjusting investment decisions based on objective criteria rather than emotions.