Yo, welcome to the showdown between growth vs value stocks! Get ready to dive into the world of finance where these two contenders go head-to-head. It’s gonna be a wild ride, so buckle up and let’s get started.
In this epic clash, we’ll break down the fundamental disparities between growth and value stocks, explore their historical performances, and uncover the secrets behind their intriguing characteristics.
Growth vs Value Stocks Overview
When it comes to investing in the stock market, one of the key decisions investors face is choosing between growth stocks and value stocks. Growth stocks are typically companies that are expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall market, while value stocks are considered undervalued and are trading at a discount compared to their intrinsic value.
Differences Between Growth and Value Stocks
- Growth stocks tend to have high price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, reflecting the market’s confidence in their future growth potential, while value stocks have lower P/E ratios, indicating they may be undervalued.
- Investors in growth stocks are often willing to pay a premium for the expectation of future earnings growth, while investors in value stocks are looking for bargains and companies that are currently trading below their true value.
Examples of Growth and Value Stocks
- Well-known growth stocks include companies like Amazon, Tesla, and Netflix, which have shown rapid revenue and earnings growth in recent years.
- On the other hand, value stocks such as Coca-Cola, Walmart, and Exxon Mobil are considered more stable and often pay dividends to shareholders.
Historical Performance of Growth vs Value Stocks
- Historically, growth stocks have outperformed value stocks during periods of economic expansion and strong market growth, as investors flock to high-growth companies with the potential for significant returns.
- However, during market downturns or periods of economic uncertainty, value stocks have often outperformed growth stocks, as investors seek safety and stability in undervalued companies with solid fundamentals.
Characteristics of Growth Stocks
Growth stocks are a type of stock in which companies are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to other companies in the market. They typically reinvest their earnings back into the company rather than paying dividends to shareholders.
Key Characteristics of Growth Stocks
- High potential for future earnings growth
- Often in innovative industries
- Higher price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios
- Low or no dividend payments
- Volatility in stock price
Why Growth Stocks Tend to Have Higher Valuations
Growth stocks tend to have higher valuations because investors are willing to pay a premium for the potential future growth of these companies. The expectation of high earnings growth leads to higher demand for these stocks, which drives up their prices.
Examples of Industries Where Growth Stocks are Commonly Found
| Industry | Examples of Companies |
|---|---|
| Technology | Apple, Amazon, Tesla |
| Biotechnology | Biogen, Moderna, Vertex Pharmaceuticals |
| E-commerce | Shopify, Alibaba, Etsy |
Characteristics of Value Stocks
Value stocks are a type of stock that is typically priced lower than what it is actually worth, making them potentially undervalued in the market. These stocks are often considered to have strong fundamentals and stable earnings, making them attractive to investors looking for long-term growth potential at a discounted price.
Key Characteristics of Value Stocks
- Low Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: Value stocks often have a low P/E ratio compared to the overall market average, indicating that the stock is undervalued relative to its earnings.
- High Dividend Yield: Value stocks tend to have higher dividend yields, which can provide investors with a steady income stream even if the stock price does not increase significantly.
- Strong Balance Sheet: Value stocks typically have solid balance sheets with low debt levels and consistent cash flow, making them less vulnerable to economic downturns.
Examples of Industries Where Value Stocks are Commonly Found
- Utilities: Companies in the utility sector often have stable earnings and cash flows, making them attractive value stocks for investors seeking steady income.
- Financial Services: Banks and insurance companies can be considered value stocks due to their historically low valuations and potential for long-term growth.
- Consumer Staples: Companies that produce essential goods like food, beverages, and household products are often seen as value stocks because of their resilient business models.
Factors Influencing Growth vs Value Investing
When it comes to choosing between growth and value stocks, there are several factors that can influence your decision. Let’s take a look at how economic conditions, interest rates, and market cycles play a role in determining whether growth or value investing may be more favorable at a given time.
Economic Conditions
In times of economic expansion and prosperity, growth stocks tend to outperform value stocks. This is because growth companies are typically able to increase their earnings at a faster pace during periods of economic growth. On the other hand, value stocks may perform better during economic downturns when investors seek more stable and established companies with solid fundamentals.
Interest Rates Impact
Changes in interest rates can have a significant impact on growth and value stocks. When interest rates are low, growth stocks become more attractive as the cost of borrowing decreases, allowing growth companies to invest in expansion and innovation. Conversely, value stocks may struggle in a low-interest-rate environment as investors seek higher returns in riskier assets. On the other hand, when interest rates rise, value stocks may become more appealing due to their stable earnings and dividends, while growth stocks may face pressure as borrowing costs increase.
Market Cycles Influence
Market cycles can also play a role in the performance of growth versus value stocks. During bull markets, growth stocks tend to shine as investors are willing to take on more risk and bet on companies with high growth potential. In contrast, during bear markets or periods of economic uncertainty, value stocks may outperform as investors flock to safer, undervalued assets. Understanding where we are in the market cycle can help investors determine whether growth or value stocks are likely to fare better in the current environment.
Risk and Return Profiles
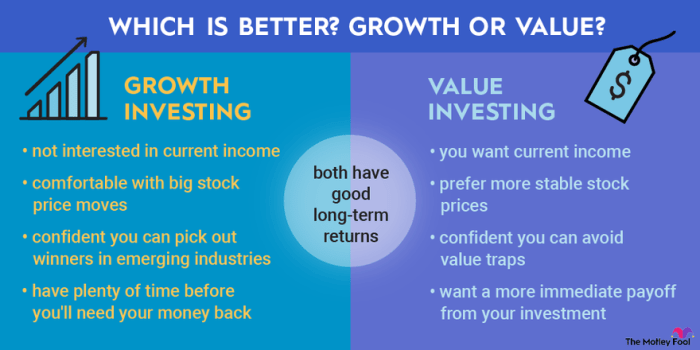
When it comes to investing in stocks, understanding the risk and return profiles of both growth and value stocks is crucial for making informed decisions. Let’s take a closer look at how these two types of stocks differ in terms of risk and return.
Risk and Return Profiles of Growth and Value Stocks
- Growth stocks typically offer higher potential returns but come with higher risk due to their higher valuations and potential for volatility.
- Value stocks, on the other hand, are often considered less risky as they are undervalued in the market, providing a margin of safety for investors.
- Investors looking for rapid capital appreciation may be drawn to growth stocks, while those seeking stable returns may prefer value stocks.
Investors’ Risk Tolerance and Preference for Growth or Value Stocks
- Investors with a higher risk tolerance may be more inclined to invest in growth stocks, as they are willing to take on the higher volatility in exchange for potentially higher returns.
- On the other hand, investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer value stocks, as they offer a more conservative investment approach with potentially lower risk.
Strategies for Balancing a Portfolio with Growth and Value Stocks
- One strategy for balancing a portfolio is to allocate a certain percentage to both growth and value stocks based on your risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Diversification is key in reducing overall portfolio risk, so including a mix of growth and value stocks can help spread out risk and capture opportunities in different market conditions.
- Regularly reviewing and rebalancing your portfolio to ensure it aligns with your risk tolerance and investment objectives is essential for long-term success.