Diving into the world of financial risk tolerance, we uncover the key elements that shape an individual’s approach to investments. From understanding the difference between risk tolerance and risk capacity to exploring the various tools used for assessment, this guide promises to shed light on a crucial aspect of financial planning.
As we unravel the complexities of financial risk tolerance, we aim to provide clarity and insight into the factors that influence one’s investment decisions.
What is Financial Risk Tolerance?
Financial risk tolerance refers to an individual’s willingness and ability to endure fluctuations in the value of their investments in pursuit of potentially higher returns. It is a crucial factor in determining an individual’s investment strategy and portfolio allocation.
Difference from Risk Capacity
Financial risk tolerance is distinct from risk capacity, which is the actual ability of an individual to take on financial risk based on factors such as income, assets, and liabilities. While risk tolerance is more subjective and psychological, risk capacity is more objective and based on financial circumstances.
Factors Influencing Financial Risk Tolerance
- Age: Younger individuals typically have higher risk tolerance as they have more time to recover from potential losses.
- Income: Higher income levels often correlate with higher risk tolerance as individuals may have more resources to withstand fluctuations.
- Investment Knowledge: Those with a deeper understanding of investing may have higher risk tolerance due to confidence in their decisions.
- Financial Goals: Individuals with long-term financial goals may be more willing to take on risk for potential growth.
- Personality: Risk tolerance can also be influenced by an individual’s personality traits, such as being risk-averse or risk-seeking.
Assessing Financial Risk Tolerance
Understanding one’s financial risk tolerance is crucial in the realm of financial planning. It helps individuals make informed decisions about their investments and ensures that their portfolios align with their comfort level when it comes to taking risks.
Methods to Assess Financial Risk Tolerance
- Questionnaires: Financial advisors often use risk tolerance questionnaires to assess an individual’s willingness to take on financial risk. These questions cover various aspects such as investment goals, time horizon, and reactions to market fluctuations.
- Psychometric Testing: Some advisors use psychometric testing to gauge risk tolerance. These tests analyze an individual’s behavioral tendencies and psychological factors that may influence their risk-taking abilities.
- Scenario Analysis: Another method involves presenting different financial scenarios to individuals to gauge their reactions and decision-making process under varying levels of risk.
Importance of Understanding Risk Tolerance in Financial Planning
- Alignment of Investments: Knowing one’s risk tolerance helps in aligning investments with personal comfort levels, preventing impulsive decisions during market fluctuations.
- Goal Setting: Understanding risk tolerance allows individuals to set realistic financial goals that match their risk appetite, ensuring a balanced approach to wealth accumulation.
- Asset Allocation: Risk tolerance influences asset allocation decisions, helping individuals create diversified portfolios that mitigate risk while aiming for returns.
Tools for Gauging Risk Tolerance
- Risk Tolerance Questionnaires: These questionnaires are widely used and readily available online or through financial advisors to help individuals assess their risk appetite.
- Online Risk Assessment Tools: Various online platforms offer risk assessment tools that provide personalized risk profiles based on individual responses to financial scenarios.
- Professional Guidance: Seeking advice from financial advisors or planners can also help individuals understand their risk tolerance through personalized assessments and discussions.
Types of Financial Risks
Financial risks come in various forms and can have a significant impact on an individual’s risk tolerance and investment decisions. Understanding these risks is crucial for navigating the financial landscape effectively.
Market Risk
Market risk refers to the possibility of investments losing value due to market fluctuations. This type of risk is inherent in all investments and can be influenced by factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, and market sentiment.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is the risk of changes in interest rates affecting the value of investments. For example, when interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, impacting the value of fixed-income securities in an investor’s portfolio.
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk of a borrower failing to repay a loan or debt obligation. This risk is prevalent in investments such as corporate bonds and can lead to financial losses if the borrower defaults on payments.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the difficulty of buying or selling an investment quickly without significantly impacting its price. Investments with low liquidity may be challenging to sell at a fair price, especially during times of market stress.
Inflation Risk
Inflation risk is the risk that the purchasing power of money will decrease over time due to rising inflation rates. This can erode the real value of investments, especially those with fixed interest rates or returns.
Reinvestment Risk
Reinvestment risk occurs when proceeds from an investment are reinvested at a lower rate of return. This risk is common in fixed-income investments when interest rates decline, leading to lower yields on reinvested funds.
Political Risk
Political risk refers to the impact of political decisions or instability on investments. This risk can arise from changes in government policies, regulations, or geopolitical events that affect the financial markets.
Currency Risk
Currency risk, also known as exchange rate risk, is the risk of investments losing value due to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates. This risk is relevant for international investments and can impact returns when the investor’s home currency strengthens or weakens against other currencies.
Operational Risk
Operational risk is the risk of financial loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, or human error. This risk can arise from various sources, including fraud, technological failures, and compliance issues.
Strategies for Managing Financial Risk
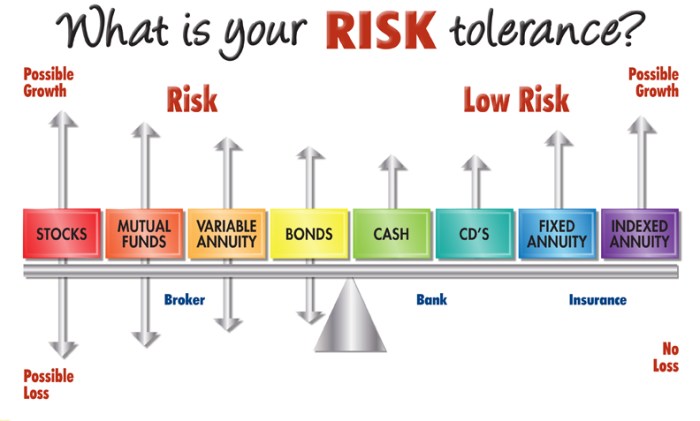
Managing financial risk is crucial for individuals looking to protect their investments and achieve their financial goals. By implementing various strategies, investors can minimize potential losses and maximize returns.
Risk-Return Tradeoff in Investment Decisions
When making investment decisions, it is essential to understand the concept of risk-return tradeoff. This principle states that the higher the risk associated with an investment, the higher the potential return. Investors must determine their risk tolerance level based on their financial goals and investment horizon.
Diversification Techniques to Mitigate Financial Risks
Diversification is a key strategy for managing financial risk. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their portfolio. Some examples of diversification techniques include:
- Asset Allocation: Allocating investments among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents to reduce overall risk.
- Industry Diversification: Investing in companies from various industries to minimize the impact of sector-specific risks.
- Geographic Diversification: Spreading investments across different regions to mitigate country-specific risks and currency fluctuations.
- Portfolio Rebalancing: Regularly reviewing and adjusting the asset allocation to maintain the desired risk level and return potential.