Hey everyone! Ready to dive into the world of student loan repayment options? Get ready to explore the ins and outs of different plans and strategies that can help you tackle that debt like a boss. So, grab your favorite drink, sit back, and let’s navigate through this financial maze together.
In the following paragraphs, we’ll break down the various student loan repayment options available to help you make informed decisions about managing your student loans.
Overview of Student Loan Repayment Options
When it comes to paying back those college loans, you’ve got options, my friend. Let’s break it down for ya.
Types of Student Loan Repayment Plans
So, there are a few different ways you can tackle those student loans. Here’s the lowdown:
- Standard Repayment Plan: This is your basic, run-of-the-mill plan where you pay a fixed amount each month until your loan is paid off. Simple and straightforward.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: These plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income, making it easier to manage if you’re not rolling in the dough just yet.
- Graduated Repayment Plan: With this plan, your payments start off low and increase every two years. Great if you’re expecting your income to rise over time.
Income-Driven vs. Standard Repayment Plans
Now, let’s compare and contrast these two popular options:
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: These plans are all about flexibility. Your monthly payments are based on a percentage of your discretionary income, which can be a lifesaver if you’re not pulling in a huge salary.
- Standard Repayment Plan: This plan keeps things simple with fixed monthly payments over a set period of time. It may cost you more in the long run, but it’s predictable and can help you pay off your loan faster.
Eligibility Criteria for Student Loan Repayment Options
Before you jump into a repayment plan, make sure you meet the eligibility requirements:
- Standard Repayment Plan: Available to all borrowers with federal student loans.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: Eligibility varies depending on the specific plan, but generally based on factors like income, family size, and loan type.
- Graduated Repayment Plan: Typically available to borrowers with federal student loans who expect their income to increase over time.
Federal Student Loan Repayment Plans
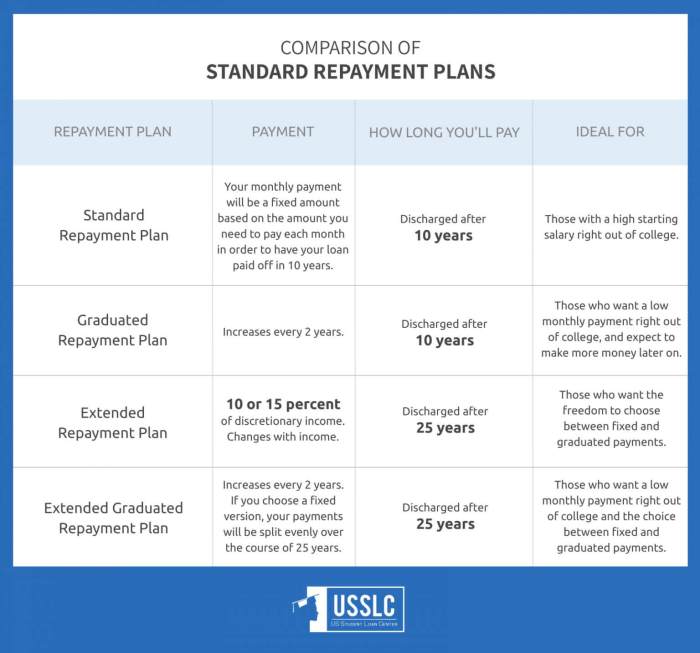
Federal student loan repayment plans offer various options for borrowers to manage their loan payments effectively. Each plan has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, so it’s essential to understand the details before choosing the right one for your situation.
Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans
Income-Driven Repayment plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income, making them more manageable. There are different types of IDR plans, such as Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), and Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE). These plans typically extend the repayment period, resulting in lower monthly payments.
Graduated Repayment Plan
The Graduated Repayment Plan starts with lower monthly payments that increase every two years. This plan is suitable for borrowers who expect their income to rise steadily over time. While the initial payments are lower, the total interest paid over the loan term may be higher compared to other plans.
Standard Repayment Plan
The Standard Repayment Plan sets a fixed monthly payment amount over a 10-year period. This plan helps borrowers pay off their loans faster and with less interest compared to other plans. However, the monthly payments may be higher than those offered by IDR plans.
Pros and Cons
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: Pros – Lower monthly payments based on income, potential loan forgiveness after a certain period. Cons – Extended repayment period, may increase total interest paid.
- Graduated Repayment Plan: Pros – Initial lower payments, suitable for increasing income. Cons – Total interest paid may be higher, payments increase over time.
- Standard Repayment Plan: Pros – Fixed 10-year repayment period, lower total interest paid. Cons – Higher monthly payments compared to IDR plans.
Applying for Federal Student Loan Repayment Plans
To apply for federal student loan repayment plans, borrowers can contact their loan servicer or apply online through the official student aid website. Each plan has specific eligibility requirements, so it’s crucial to review them carefully before submitting an application.
Private Student Loan Repayment Options
When it comes to private student loan repayment options, there are some key differences compared to federal options. Private loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and online lenders, while federal loans are funded by the government. Private loans usually have higher interest rates and fewer repayment plan options than federal loans. However, private loans can be a good option for students who have maxed out their federal loan options and still need additional funding for school.
Differences Between Federal and Private Student Loan Repayment Options
- Private loans have higher interest rates compared to federal loans.
- Private loans offer fewer repayment plan options.
- Federal loans offer more borrower protections and forgiveness programs.
Examples of Private Lenders Offering Student Loan Repayment Options
- Sallie Mae
- Discover Student Loans
- Wells Fargo
Strategies for Managing and Repaying Private Student Loans Effectively
- Create a budget and stick to it to ensure you can make your monthly payments.
- Consider refinancing your private loans to secure a lower interest rate.
- Look into income-driven repayment plans offered by some private lenders.
- Communicate with your lender if you’re struggling to make payments to explore alternative options.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
When it comes to managing student loan debt, loan forgiveness programs can be a saving grace for many borrowers. These programs provide an opportunity to have a portion or all of your student loans forgiven under certain circumstances.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
- PSLF is a program designed for borrowers who work in qualifying public service jobs.
- Eligibility requirements include working full-time for a government or non-profit organization and making 120 qualifying payments under an income-driven repayment plan.
- After meeting the requirements, the remaining balance on your Direct Loans may be forgiven tax-free.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness
- This program is specifically for teachers who work in low-income schools or educational service agencies.
- To qualify, teachers must teach full-time for five consecutive years and meet other specific requirements.
- Depending on the subject taught, eligible teachers can receive forgiveness of up to $17,500 on their Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans.
Success Stories
“I was able to have over $50,000 in student loans forgiven through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program after working for a non-profit organization for ten years. It was a huge relief and allowed me to pursue my passion without the burden of debt.”
“As a teacher in a low-income school, I qualified for the Teacher Loan Forgiveness program and had $17,500 forgiven on my student loans. It was a great incentive to continue teaching in an underserved community.”
Consolidation and Refinancing
When it comes to managing student loan debt, consolidation and refinancing can offer potential solutions for borrowers looking to simplify their repayment process or secure better terms. Consolidation involves combining multiple loans into a single loan with one monthly payment, while refinancing entails obtaining a new loan with different terms to replace existing loans.
Loan Consolidation
- Loan consolidation allows borrowers to streamline their payments by combining multiple federal loans into a single loan.
- Consolidation can potentially lower monthly payments by extending the repayment period, but may result in paying more interest over time.
- It may also open up access to income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs for federal loans.
Loan Refinancing
- Refinancing involves taking out a new loan with a private lender to pay off existing student loans, typically with a lower interest rate and/or better terms.
- Borrowers with good credit and stable income may qualify for lower interest rates through refinancing.
- Refinancing federal loans with a private lender means losing access to federal loan benefits like income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs.
It’s important to carefully consider the pros and cons of consolidation and refinancing before making a decision.